What is Remote Learning? A Complete Guide
The world of education has changed dramatically over the last decade. Traditional classrooms are no longer the only way to learn. With the rise of technology, students now have access to new learning methods, one of the most popular being remote learning.
But what is remote learning exactly? How does it differ from online learning or distance education? And why has it become such a crucial part of modern education?
In this guide, we’ll explore in detail—its meaning, how it works, its advantages and challenges, and practical tips for making it effective. Whether you’re a student, parent, or educator, this article will help you understand everything you need to know about.
What is Remote Learning?
At its core, remote learning means learning that takes place outside of a traditional physical classroom. Instead of sitting in a school or university building, students engage with lessons through digital tools, video conferencing, and online resources.
It allows learners and teachers to connect virtually—using platforms like Zoom, Microsoft Teams, or Google Classroom—so education continues regardless of location.
In simple words:
👉 Remote learning = education without being physically present in a classroom.
This type of learning became especially popular during the COVID-19 pandemic, when schools worldwide had to close their doors. However, it’s not just a temporary solution; it’s a growing educational model that is here to stay.
Remote Learning vs. Online Learning vs. Distance Learning
Many people confuse these terms, so let’s break them down clearly:
Remote Learning: A broader approach where students and teachers are physically separated, using technology to communicate. It often mirrors in-person classes but in a virtual environment.
Online Learning: A subset of that happens entirely on the internet. For example, self-paced online courses on platforms like Coursera or Udemy.
Distance Learning: A more traditional version of remote education, often involving recorded lectures, mailed materials, or pre-scheduled TV/radio broadcasts, with less real-time interaction.
In short:
= live, teacher-led but virtual.
Online learning = digital, self-paced or guided.
Distance learning = more independent, less interactive.
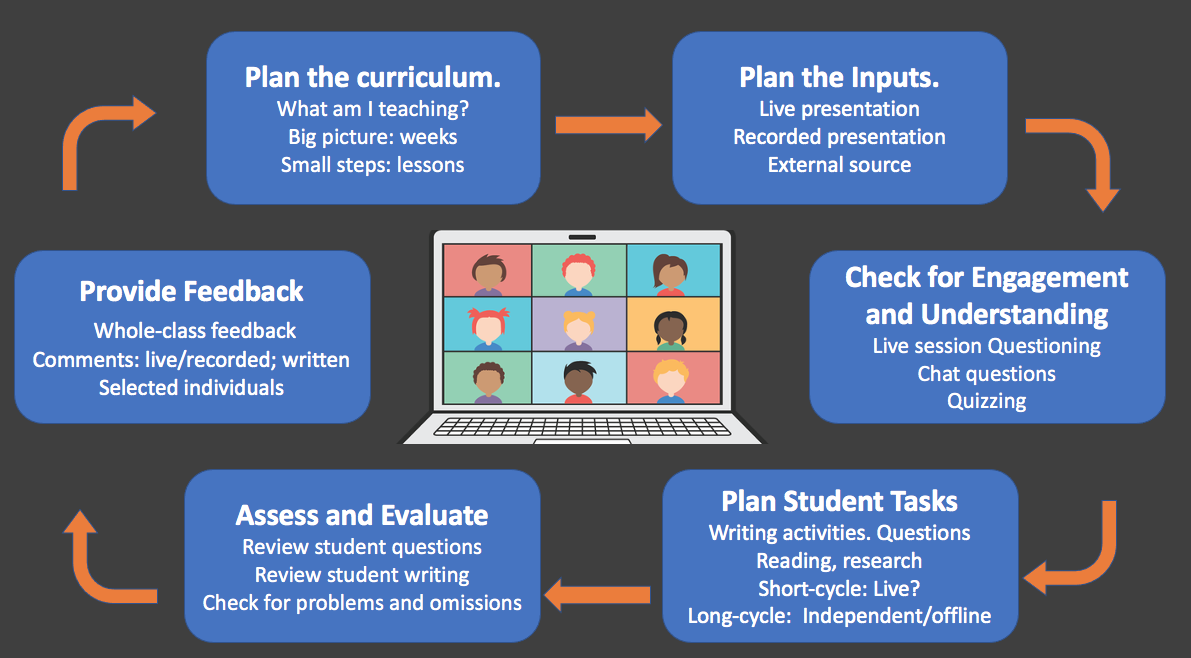
How Does Remote Learning Work?
relies heavily on digital tools and structured planning. Here’s how it typically works:
Digital Platforms: Schools or institutions use platforms like Zoom, Google Meet, or Microsoft Teams to conduct live classes.
Learning Management Systems (LMS): Systems like Moodle, Blackboard, or Google Classroom store assignments, notes, and grades.
Communication Tools: Email, chat groups, and discussion forums help teachers and students stay connected.
Content Delivery: Lessons may include live lectures, recorded videos, presentations, quizzes, and interactive exercises.
Assessment: Students submit assignments online, take digital quizzes, and sometimes even give virtual presentations.
Example: A high school student attends math class via Zoom, watches a pre-recorded video for homework, and submits answers to an online quiz through Google Classroom.
Benefits of Remote Learning
has many advantages, making it popular worldwide:
Flexibility
Students can learn from anywhere, whether at home, in a library, or while traveling.
Accessibility
It opens doors for people who may not have access to quality education in their local area.
Cost-Effective
No commuting, fewer physical resources, and reduced costs for schools and families.
Personalized Learning
Students can revisit recorded lessons, pause and replay lectures, or use additional resources to learn at their own pace.. Tech-Savvy Skills
Students naturally improve their digital literacy while engaging with online platforms and tools.
Challenges of Remote Learning
Of course, is not without its struggles. Some common challenges include:
Lack of Face-to-Face Interaction
Students may feel isolated without physical classroom engagement.
Technology Barriers
Not all students have reliable internet, laptops, or quiet study spaces.
Distractions at Home
Learning from home can sometimes lead to reduced focus due to family, social media, or other interruptions.
Reduced Hands-On Learning
Subjects like science labs, art, or physical education are harder to teach virtually.
Motivation Issues
Without direct supervision, some students struggle to stay disciplined.
Remote Learning Tools and Technologies
To understand what remote learning really involves, it’s important to know the key tools that support it:
Video Conferencing Tools: Zoom, Microsoft Teams, Google Meet.
Learning Management Systems (LMS): Moodle, Blackboard, Canvas, Google Classroom.
Collaboration Apps: Slack, Trello, Asana.
\Interactive Tools: Kahoot!, Quizlet, Mentimeter.
Content Platforms: YouTube, Coursera, Khan Academy.
These tools make more interactive, engaging, and efficient.
Best Practices for Successful Remote Learning
Here are some practical tips for students and teachers to get the most out of:
For Students:
Create a dedicated study space.
Stick to a daily schedule.
Take regular breaks to avoid screen fatigue.
Actively participate in class discussions.
Ask questions when in doubt.
For Teachers:
Use interactive elements (polls, quizzes, group work).
Keep lessons short and focused.
Provide clear instructions and deadlines.
Encourage group projects for collaboration.
Be available for extra support when needed.
Remote Learning in Schools and Universities
Different levels of education use remote learning differently:
Elementary and High Schools: Teachers try to replicate classroom experiences online with live sessions and interactive activities.
Universities: Many offer blended models, mixing online lectures with occasional on-campus activities.
Corporate Training: Companies now use for professional development, onboarding, and upskilling employees.
Example: Some universities have introduced “hybrid classrooms,” where students can choose to attend physically or remotely.
The Future of Remote Learning
The question “what is remote learning” is not just about understanding the present—it’s also about looking into the future.
Experts believe will continue to grow, especially as technology improves. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are expected to make online classes more immersive, while Artificial Intelligence (AI) will personalize learning experiences.
Education may soon become a global marketplace, where students from any part of the world can access the best teachers and courses without geographical limits.
Case Study: Remote Learning During COVID-19
When the COVID-19 pandemic forced schools to close, millions of students worldwide turned to remote learning.
In the U.S., more than 55 million students shifted to online classes.
Countries like China launched large-scale online education platforms.
Teachers adapted quickly, learning new tools to keep students engaged.
This period proved that while had challenges, it was an essential lifeline for education continuity.
FAQs About Remote Learning
1. What is the main difference between remote learning and online learning?
often mirrors traditional classes but virtually, while online learning can be fully self-paced.
2. Can remote learning replace traditional classrooms?
Not entirely. It complements traditional education but face-to-face learning remains important for certain skills.
3. Is remote learning effective?
Yes, when structured well. It works best with interactive tools, disciplined students, and supportive teachers.
4. Do students need high-speed internet for remote learning?
A stable connection is important, but many platforms allow low-bandwidth access as well.
Conclusion
So, what is remote learning? In simple terms, it’s learning that happens outside of the physical classroom, powered by technology, and designed to make education flexible and accessible.
It has transformed education by making learning possible from anywhere, anytime. While it comes with challenges like isolation and technical barriers, the benefits—flexibility, accessibility, and global opportunities—are undeniable.
is not just a temporary solution; it’s the future of education. Whether you’re a student exploring new opportunities, a teacher adapting to digital tools, or a parent guiding your child, embracing can open new doors to knowledge and growth.
Final Thought: The question isn’t whether is here to stay—it’s how we can make it better, more inclusive, and more effective for everyone.













Post Comment